When it comes to education, grading is an essential part of measuring student performance. But not all grading systems are the same. Around the world—and even within the same country schools and teachers use different grading scales to evaluate academic achievement. Understanding these scales can help teachers grade fairly and students interpret their results more accurately.
1. The Percentage Grading Scale
One of the most common systems is the percentage grading scale. It converts a student’s performance into a percentage out of 100. For example, a student scoring 85% on a test would fall into a specific letter grade, depending on the school’s grading system. This method is easy to understand and calculate using tools like Easy Grader or Quick Grade calculators, which automatically convert scores into percentages.
2. The Letter Grading Scale
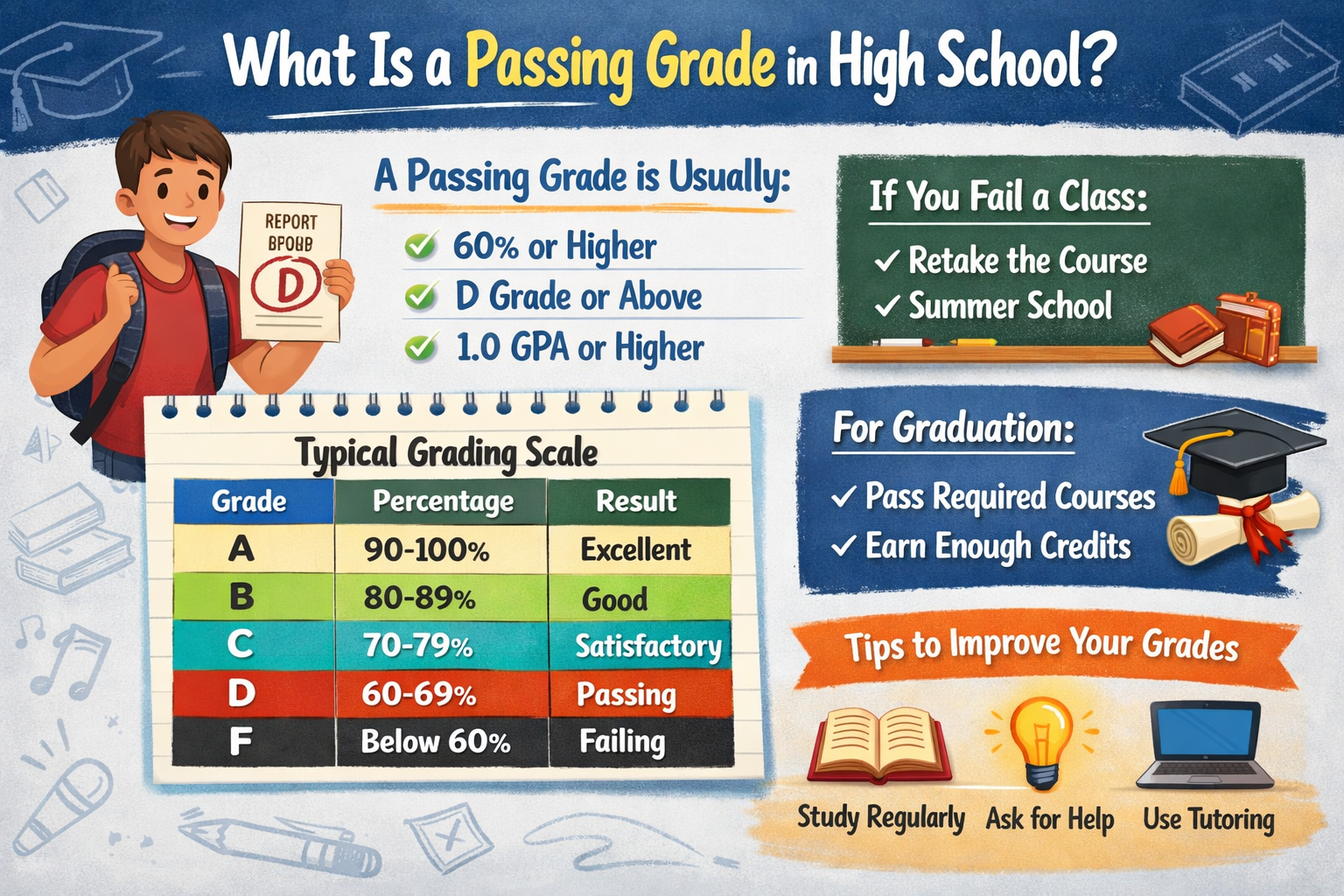
The letter grade scale is often used alongside percentages. For example:
- A = 90–100%
- B = 80–89%
- C = 70–79%
- D = 60–69%
- F = below 60%
This system makes it simple to categorize student performance into broader levels of achievement. Teachers often use grading calculators or online graders to quickly assign letter grades without manual conversion errors.
3. The GPA (Grade Point Average) Scale
The GPA scale is widely used in colleges and universities. Each letter grade corresponds to a point value—commonly on a 4.0 scale:
- A = 4.0
- B = 3.0
- C = 2.0
- D = 1.0
- F = 0.0
Students’ GPAs are then averaged over time to reflect their overall academic performance. Many teacher grade calculators and EZ grader tools help educators and students convert grades into GPA automatically, saving valuable time.
4. Weighted vs. Unweighted Scales
Some institutions use weighted grading scales to reward students taking advanced or honors courses. For instance, an A in an honors class might equal 5.0 instead of 4.0 on the GPA scale. In contrast, unweighted scales treat all courses equally. Understanding the difference helps students set realistic goals and teachers assign fair grades.
5. Standards-Based Grading (SBG)
A modern approach to grading, Standards-Based Grading focuses on mastery of specific learning objectives instead of cumulative scores. Instead of letter grades, students might receive feedback like “Exceeds Expectations,” “Meets Expectations,” or “Needs Improvement.” This method promotes learning over competition but requires detailed tracking, which can be simplified using digital grading calculators.
Conclusion
Grading scales may vary, but their purpose remains the same—to evaluate and communicate student performance. Whether you use a quick grader, online grade calculator, or a teacher’s EZ grader, understanding these different systems ensures transparency and consistency in assessment. As education evolves, digital grading tools like EasyGraders.com make it simpler than ever to calculate grades accurately, no matter which scale you use.