Grading charts are integral tools in education. Used by educators to assess student performances and assign grades, understanding grading charts can significantly enhance how one views academic achievements and progress. We will explore why they exist as well as different grading systems used across education environments in this article.
What Is a Grading Chart?
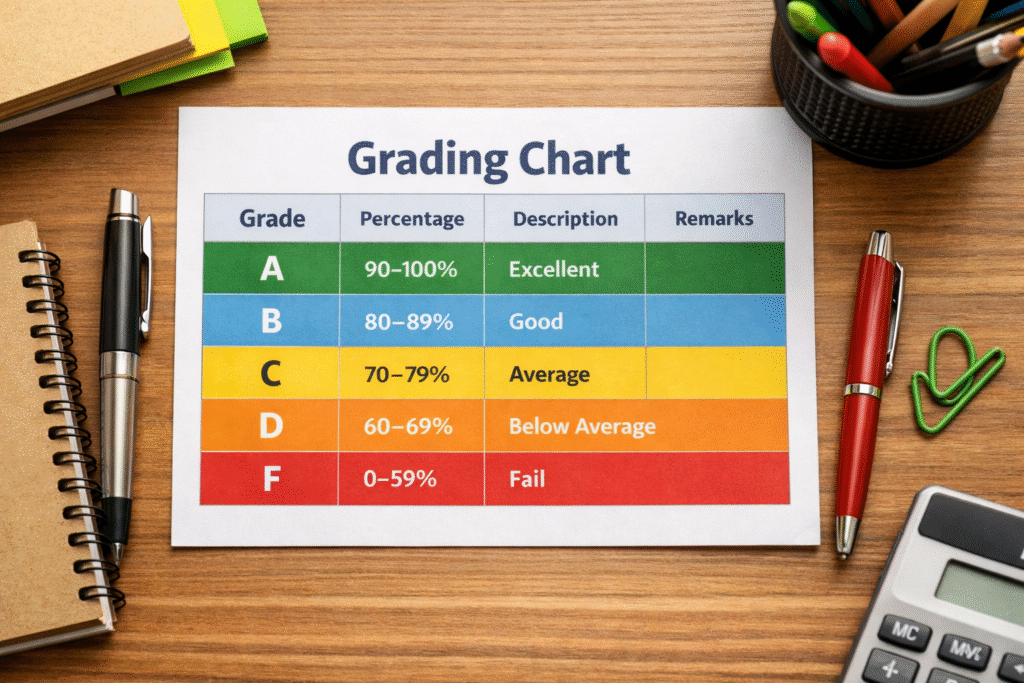
Provide teachers with a visual representation of how Quick grader are assigned based on students’ scores or performance, making the assessment process simpler for both them and students. Grade schemes usually consist of letter grades (A, B etc), numerical scores such as 90-100 for an A grade as well as percentage ranges for uniform grading across classes and students.
Assuming the American system is in use, an example grading scale chart may look something like this:
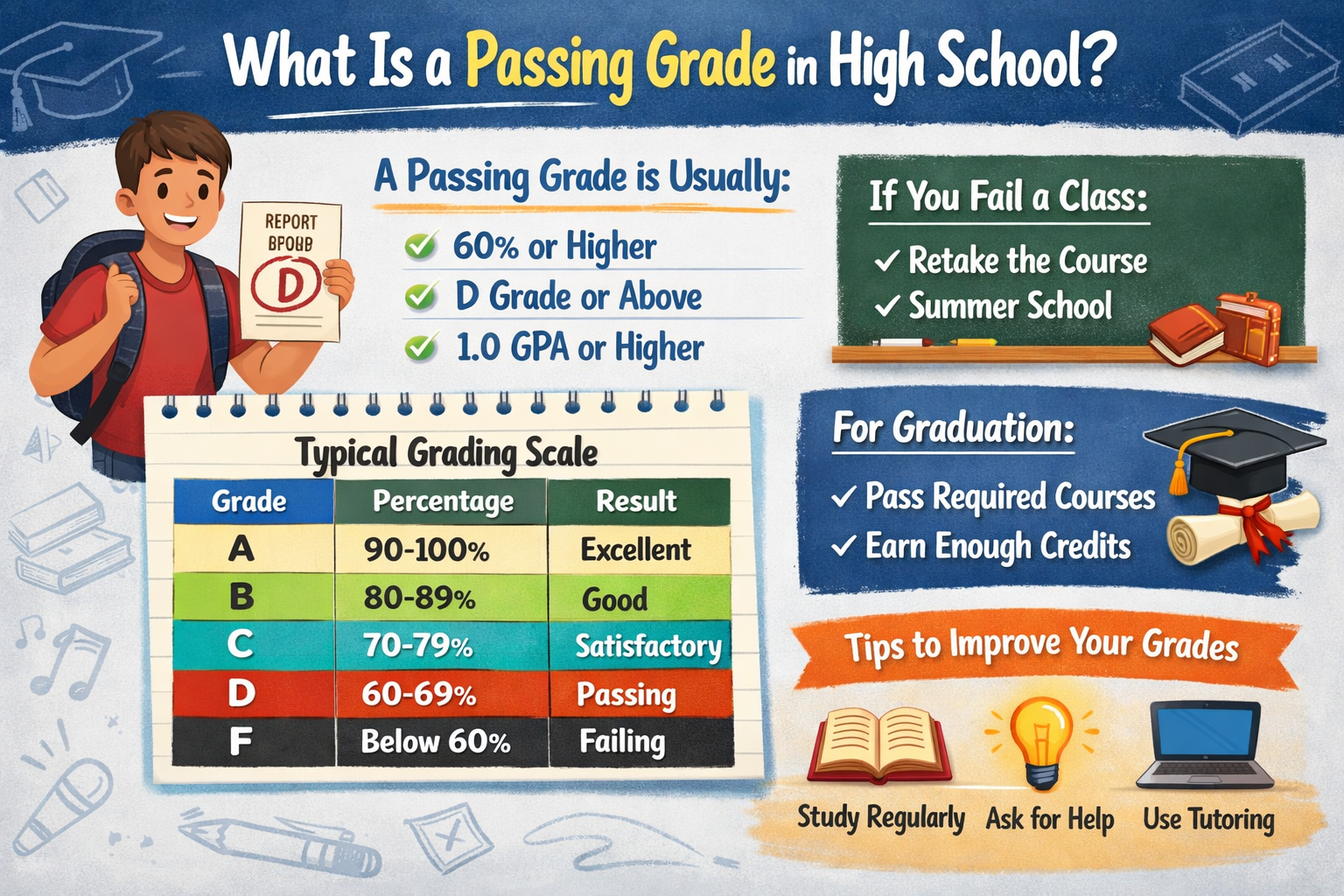
| Percentage Range | Letter Grade | GPA |
| 90-100% | A | 4.0 |
| 80-89% | B | 3.0 |
| 70-79% | C | 2.0 |
| 60-69% | D | 1.0 |
| Below 60% | F | 0.0 |
Why Are Grading Charts Important?
Grading charts are clear and provide the ability to evaluate students’ academic performance. They enable students to comprehend what they must do in order to earn certain grades. Furthermore, the charting grades:
- Make sure that teachers use the same guidelines for grading every student and minimize the possibility of biases.
- Set clear expectations for students and parents can easily decide the percentage or performance grade is required to earn a grade.
- Aid with making decisions Grading charts can be utilized to make critical academic decisions, like promotion, scholarships, and graduation requirements.
Explore More: 16/20 grade
Types of Grading Systems
While the Grading Chart is a popular tool for schools around the world Different regions and institutions might utilize different systems for grading. Here are a few of the most popular methods of grading:
1. The American Grading System
This is typically based on letters grade (A up to F) in conjunction alongside GPA (Grade Point Average) scales. It is believed that the 4.0 scale has the highest value and is a popular scale, in which an A indicates outstanding performance while an F is a sign of failure. In certain organizations, there’s different grades (A+ B-, A+, etc.) which offer greater specificity.
2. The British Grading System
In the UK the UK, grades are typically given based on letters like A, A B D, E, and* A, with a letter of ‘A’ indicating good while an “E’ signifying an A grade. The grading scales in the UK also include categories like First Class or Higher Second Class (2:1) or the Lower Second Class (2:2) for university degrees.
| Grade | Description |
| A* | Outstanding |
| A | Excellent |
| B | Good |
| C | Satisfactory/Pass |
| D | Barely Passed (Fail) |
| E | Fail |
3. The International Baccalaureate (IB) Grading System
The IB system uses a scale of 1 to 7, with 7 being the highest possible grade. IB students are also given a separate score for their Extended Essay (EE) and Theory of Knowledge (TOK) components. The total possible score is 45.
| IB Grade | Description |
| 7 | Excellent |
| 6 | Very Good |
| 5 | Good |
| 4 | Satisfactory |
| 3 | Mediocre/Pass |
| 2 | Poor/Fail |
| 1 | Very Poor/Fail |
4. The European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS)
In the ECTS, grades are typically awarded based on a scale from A to F, similar to the American grading system, but with some differences:
| Grade | ECTS Grade Description |
| A | Excellent |
| B | Very Good |
| C | Good |
| D | Satisfactory |
| E | Pass |
| F | Fail |
How to Interpret a Grading Chart
The ability to comprehend grading chart for teachers and students alike. Below are few suggestions on how to present one efficiently:
- Make sure you know your grades boundaries. Make sure you review the grades boundaries for each subject or course in order to understand that different instructors could be different in their expectations of what is considered a pass or a high grades.
- Your GPA shows your academic progress by way of a numerical representation. Higher GPA typically indicates higher academic performance. Certain universities might impose GPA prerequisites for graduation or consideration for scholarships.
- To make the best use of your efforts in school, understanding percentage ranges is key in attaining your desired grade. For instance, 92% may get you an A grade. Make sure you know which range corresponds with which letter grade.
- Some schools or universities employ a plus/minus system (A+, B-, etc) which may have the effect of slightly altering your GPA; therefore it’s essential that you remain aware of such differences within your grading chart.
Read More: 18/20 grade
Tips for Improving Your Grade Based on a Grading Chart
If you’re looking to boost your academic skills, these are some tips to help:
- If a particular subject or topic leaves you feeling confused or bewildered, take the time to research and expand on what knowledge there may be available on it.
- Regular repetition and practice will increase efficiency and help increase scores over time.
- Take your feedback seriously, and use it to enhance the quality of your work. Use our system as a source of guidance when doing homework assignments or taking tests – take seriously our feedback to improve upon yourself!
- Create an organized schedule of quizzes, assignments, homework and tests in order to stay on top of deadlines and marks. A good plan will keep everything under control!
Also Check: 12/15 grade
Conclusion
Grading charts serve a valuable function beyond classroom instruction – they serve as invaluable guides for students on what is expected of them and how their work is evaluated. By understanding different grading systems, interpreting grades correctly and employing strategies for improvement to ensure academic success – whether in elementary school or seeking higher education degrees; grading charts will always prove indispensable resources in your educational journey.